| (1) |
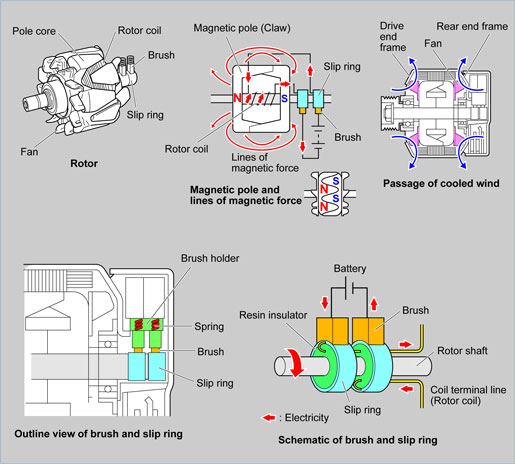
The rotor is a rotating magnet positioned inside the stator coils that produces the magnetic field to generate an electromotive force in the stator coils. The rotor coil is wound around six pairs (12 poles) of pole cores (magnetic pole) and these become an electromagnet when current flows in the coil.
As the current flowing in the rotor increases, the electromagnetic force increases. |
| (2) |
Fan blades are integrated on both ends of the rotor to draw cooling air over the rotor coil, the stator coils and the rectifier. This maintains the operating temperature of the alternator assembly by drawing air through the ventilation ports in the end frames due to the rotor's movement. |
|