| 1. |
What is refrigerant?
|
Refrigerant is a heat exchanging substance that circulates in the refrigerant cycle. It removes the heat when it evaporates and releases its heat when it liquefies.
At present, HCF-134a (R134a) is used as a refrigerant in automotive applications. |
| 2. |
Required condition of refrigerant
|
| The requirements of the refrigerant used in automotive A/C systems are; |
 |
Easy to evaporate and liquidise . |
 |
Safe and non toxic . |
 |
Chemically stable (refrigerant quality does not change) |
|
| 3. |
Characteristics of refrigerant
|
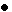
The graphic on the left shows the pressure and temperature relationship of HCF-134a (R134a).
At low pressure, HCF-134a evaporates at a low temperature, but as the pressure increases, it remains in a liquid state even at relatively high temperatures.
The car A/C system utilizes these characteristic, including liquidising the refrigerant by increasing the refrigerant pressure through the use of a compressor.
As an example, if we cool the refrigerant compressed by the compressor from the temperature / pressure intersection of 70°C and 1.47MPa by approximately 12 or 13°C, we are able to change the refrigerant state from a gas to a liquid. (This is the function of the A/C system condenser). |