|
|
 |
 |
|
Refrigeration Cycle
|
Refrigerant (Reference)
|
|
|
| 1. |
CFC-12
|
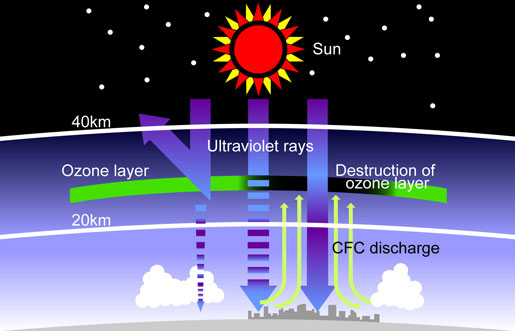
Refrigerant type CFC-12 (R12) had been used for automotive A/C systems up until 1995. However, CFC-12 (R12) was found to destroy the ozone layer when it is released into the atmosphere. The depletion of the ozone layer increases the amount of ultraviolet rays from the sun that reach the earth, increasing the incidents of diseases such as skin cancer as well as causing environment destruction, and this has become a global problem.
Presently, refrigerant HFC-134a (R134a) that does not include the substances that destroy the ozone layer is used for automotive A/C systems. If any part of the A/C system needs to be replaced or repaired, it is a legal requirement under Australian law to recover the entire refrigerant from the system, regardless of the type of refrigerant that is being used.
However, if refrigerant HFC-134a (R134a) is correctly recovered with a refrigerant recovery machine, the refrigerant is able to be recycled without reducing the system performance when it is reused. |
| 2. |
Retrofit
|
| An A/C system designed for use with refrigerant HFC-134a (R134a) is not compatible with that designed for use with CFC-12 (R12) however, it is possible to “retrofit” most CFC-12 (R12) automotive A/C systems with compatible components such as hoses, O-rings and compressor oil to convert CFC-12 (R12) vehicles to adopt HFC-134a (R134a) type refrigerant. |
|
(16)
|
|