|
|
 |
 |
|
Outline
|
Description
|
|
|
| 1. |
Description of starter motor
|
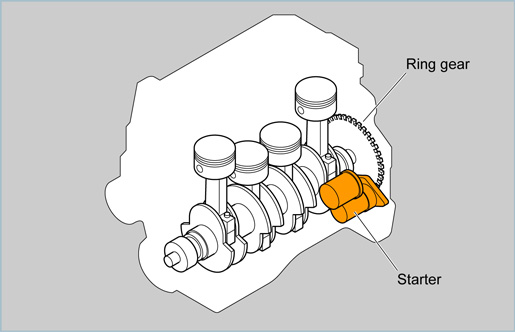
Since the engine cannot start by itself, external power is required to rotate the engine with sufficient speed to allow the initial combustion to take place. To start the engine, the starter rotates the crankshaft via the ring gear attached to the circumference of the flywheel.
The starter is required to generate extremely large torque from the limited power available from the battery and should be compact and light-weight as well. For this reason, a DC (direct current) series motor* is used for the starter motor.
To start the engine, the crankshaft has to rotate faster than the minimum cranking speed. The minimum cranking speed required to start the engine differs depending on the engine's construction and operating conditions, but it is generally 40 to 60 RPM for a gasoline engine and 80 to 100 RPM for a diesel engine. |
*DC (direct current) series motor
The DC (direct current) series motor consists of the field coil and the armature coil connected in series, and it is used to generate maximum torque as the starter begins to rotate.. |
|
(1)
|
|