|
|
 |
 |
|
Outline.
|
Alternator with Neutral-Point Voltage
|
|
|
| 1. |
Neutral-point voltage
|
| (1) |
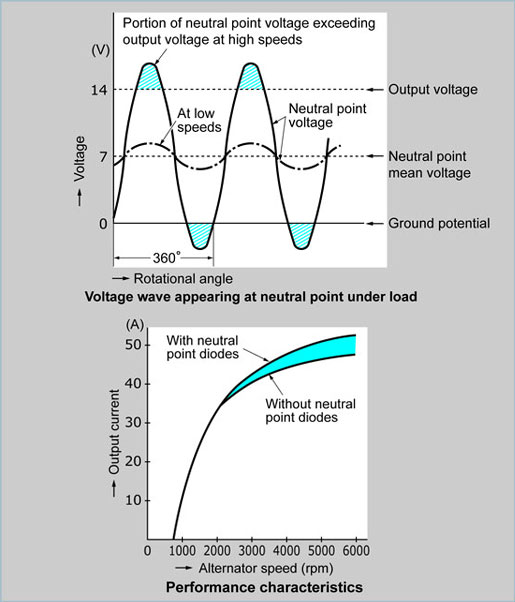
A conventional alternator uses six diodes to rectify three-phase AC (Alternating Current) into DC (Direct Current). The output voltages generated at the neutral point can be utilized as a power source for the charge warning light relay. It is known that the average voltage of the neutral point is one half of the output DC voltage. While stator current (output current) is flowing through the alternator, the voltage at the neutral point is mostly DC, however it also includes an AC portion.
This AC portion is induced in each phase by the flow of output current. When the alternator speed exceeds 2,000 to 3,000 rpm, the peak value of this AC portion exceeds the DC output voltage. |
| (2) |
This means that, compared with the output characteristics of an alternator without neutral-point diodes, the output gradually increases from about the mid speed point by 10 to 15% for a normal alternator with a rated speed of 5,000 to 6,000 rpm. |
|
|
(12)
|
|