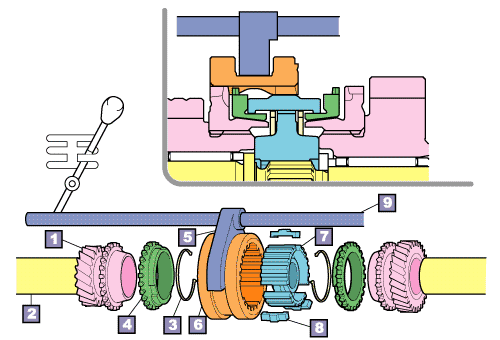
When the shift lever is operated, the synchronizer ring is pressed against the gear cone, causing the gear rotation speed to increase or decrease accordingly.
This eliminates the difference in speed between the shift gear and the sliding hub, allowing gear engagement to take place.
Consequentially, the friction between the gear cone and ring gradually wears down the inner wall of the synchronizer ring. As the wear increases, the gap between the gears decreases causing the synchronizer ring to slip and disrupting smooth gear meshing.
|
|
Inspection |
Inspect Synchronizer Ring |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
(11) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||