|
|
 |
 |
|
Outline
|
Ordinary Diode
|
|
|
| 1. |
Description
|
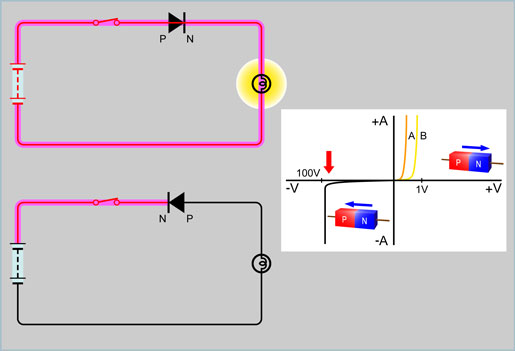
| An ordinary diode allows a current to flow
only in one direction: from the p-side to
the n-side. |
| 2. |
Characteristics
|
A minimum voltage is required before the current will flow from the p-side to the n-side. The required voltage depends on the semi conductor material used in the construction of the diode however the general required voltage is about 0.3V to 0.7V.
The current will not flow if a voltage is applied in the opposite direction (Note: practically, an extremely small current does flow, called the reverse leakage current, however it is not considered as flowing current because it does not affect the operation of the actual circuit).
However, if the voltage applied in the opposite direction is sufficiently increased, the amount of current allowed to pass through the diode will suddenly increase, causing failure in the ordinary rectifying diode. This phenomenon is called diode breakdown, and the amount of voltage that is applied for this breakdown to occur is called the breakdown voltage. |
|
(9)
|
|